45 nucleotide label
Question : Classify the compound as a nucleoside or nucleotide. Label ... We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: Classify the compound as a nucleoside or nucleotide. Label its components and name the compound. Nucleoside Classification: Nucleotide NH2 Adbose Adenosine 5- monophosphate 'N 2-Deoxyribose Guanine HO-CH2 N N monophosphate DEuangsing Filme Guanosine ... Peptide and Nucleotide Labeling | SCBT - Santa Cruz Biotechnology Peptide and Nucleotide Labeling. Peptide and Nucleotide Labeling biochemicals from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. have many applications in biochemical and biomedical research. Click on the product of choice to view detailed information such as the chemical structure and specific chemical properties. In stock Peptide and Nucleotide Labeling ...
Nucleotide labeled structure Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Nucleotide labeled structure. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Nucleotide label
Biotin Labels Products | NEB Biotin Labels. For optimal flexibility with existing technologies, biotinylated labels are available for studies using streptavidin platforms. Cell-permeable SNAP-Biotin and CLIP-Biotin are suitable for applications such as biotinylation of fusion proteins in or on living cells for detection with streptavidin fluorophore conjugates or labeling in solution for analysis by SDS-PAGE/Western blot. The Structure of DNA The Structure of DNA. This figure is a diagram of a short stretch of a DNA molecule which is unwound and flattened for clarity. The boxed area at the lower left encloses one nucleotide. Each nucleotide is itself make of three subunits: A phosphate group (a phosphorous atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms.) (Labeled P) And one of four nitrogen ... Labeling Oligonucleotides and Nucleic Acids—Section 8.2 the labeled aha-dutp and aha-dctp nucleotides can be used to generate labeled nucleic acid hybridization probes for many molecular biology and molecular cytogenetics applications, including two-color microarray assays, northern and southern blots, colony and plaque hybridizations, dna sequencing, primer extension, dna and rna amplification and …
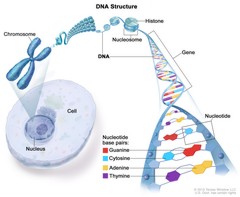
Nucleotide label. Nucleotide - Genome.gov A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA). A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). Home - Nucleotide - NCBI The Nucleotide database is a collection of sequences from several sources, including GenBank, RefSeq, TPA and PDB. Genome, gene and transcript sequence data provide the foundation for biomedical research and discovery. Using Nucleotide Quick Start Guide FAQ Help GenBank FTP RefSeq FTP Nucleotide Tools Submit to GenBank LinkOut E-Utilities BLAST Use the drop-down menus to label the parts of a nucleotide. Labels A and F correspond to phosphate groups, label B corresponds to a deoxyribose sugar, label E corresponds to a ribose sugar, and labels C and D correspond to nitrogenous bases.. DNA is a double-stranded molecule composed of two long opposite chains of nucleotides, while RNA consists of only one long chain of nucleotides.; A nucleotide is a molecule composed of a pentose sugar (ribose in ... Fluorescent and Hapten Labeled Nucleotides | PerkinElmer Labeled nucleotides are critical elements for sequence detection in a wide variety of techniques including in situ hybridization, microarrays and DNA sequencing. Our fluorescent and hapten labeled nucleotides provide a reliable, sensitive alternative to working with radioactivity through both direct and indirect detection methods.
Use the drop-down menus to label the parts of a nucleotide. Label A ... Use the drop-down menus to label the parts of a nucleotide. Label A Label B Label C Label D Label E Label F Label A is a blue circle, label B is a grey hexagon, label C is adenine, label D is uracil, label E is a pink hexagon, and label F is a blue circle. Advertisement Answer 5.0 /5 22 jarahquiroga Answer: A and F are phosphate groups The 5 Kinds of Nucleotides - ThoughtCo The five bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil, which have the symbols A, G, C, T, and U, respectively. The name of the base is generally used as the name of the nucleotide, although this is technically incorrect. The bases combine with the sugar to make the nucleotides adenosine, guanosine, cytidine, thymidine, and uridine. Nucleotide - Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. Methods for Labeling Nucleic Acids - Thermo Fisher Scientific Methods for Labeling Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids may be modified with tags that enable detection or purification. The resulting nucleic acid probes can be used to identify or recover other interacting molecules. Common labels used to generate nucleic acid probes include radioactive phosphates, biotin, fluorophores and enzymes.
3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected Nucleotides are the building blocks of the DNA and RNA used as genetic material. Nucleotides also are used for cell signaling and to transport energy throughout cells. You may be asked to name the three parts of a nucleotide and explain how they are connected or bonded to each other. Here's the answer for both DNA and RNA . What are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide? | Albert.io Figure 2: The chemical assembly of the three parts of the nucleotide, the phosphate (blue box), nitrogenous base (red box) and the pentose sugar. This particular nucleotide is adenine. The assembly of nucleotides (1) differentiates them from nucleosides, which do not contain a phosphate group (in the blue box); (2) allows the nucleotide to ... Exam 4 61. Draw a nucleotide and label all parts. (see lecture notes) 61. Draw a nucleotide and label all parts. (see lecture notes) Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. Nucleotide - Wikipedia In experimental biochemistry, nucleotides can be radiolabeled using radionuclides to yield radionucleotides. 5-nucleotides are also used in flavour enhancers as food additive to enhance the umami taste, often in the form of a yeast extract. Contents 1 Structure 2 Synthesis 2.1 Pyrimidine ribonucleotide synthesis 2.2 Purine ribonucleotide synthesis
How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? 19 Jul 2017 — The above structure is a nucleotide . It consists of a: phosphate group ...1 answer · See below Explanation: The above structure is a nucleotide. It consists of a: • phosphate group • ...
Nucleotide: Structure, Examples and Function - BYJUS A nucleotide is an organic molecule with a basic composition of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar and phosphate. DNA and RNA are polynucleotides, which contain a chain of nucleotides monomers with different nitrogenous bases. Nucleotides are essential for carrying out metabolic and physiological activities.
Nucleotide Structure: DNA Diagram | Science Trends Nucleotides are molecules which serve as the building blocks, or monomer units, for the creation of important polymers like ribonucleic acid or RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA. As mentioned, nucleotides have three component parts: a five-sided carbon sugar, a nitrogen-containing base, and a phosphate group.
Nucleotide and Structural Label Identification in Single RNA Molecules ... Here we present a method for direct nucleotide identification and structural label mapping of single RNA molecules via Quantum Molecular Sequencing (QMSeq). The method combines non-perturbative quantum tunneling spectroscopy to probe the molecular orbitals of ribonucleotides, new experimental biophysical parameters that fingerprint these ...
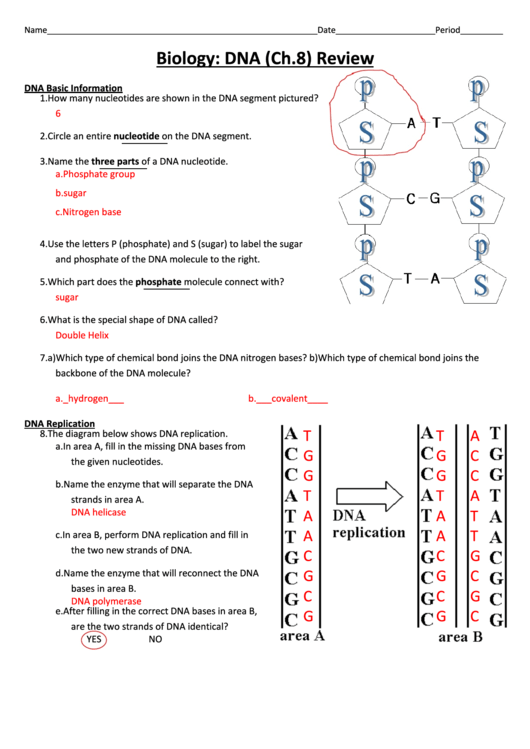
Draw a dna nucleotide an rna nucleotide label each of Draw a dna nucleotide an rna nucleotide label each of Draw a DNA nucleotide & an RNA nucleotide. Label each of the 3 major parts. 2. What are the three major differences between DNA & RNA? 3. What is the purpose of DNA replication? ____________________________ 4. When & where does replication occur? _____________________________ 5.
dna-labeling | NEB A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate nucleic acids labeled with radioactive phosphates, fluorophores, or nucleotides modified with biotin or digoxygenin for example. Nucleic acids may be labeled at their 5´ end, their 3´ end, or throughout the molecule depending on the application.
Nucleotides | Types, Examples, Functions & Classification Nucleotides are the biological molecules that serve as the building blocks of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. They are essential for all the functions performed by a living cell. Not only this, but they are also essential for transferring information to new cells or the next generation of the living organisms.
DNA and RNA Probe Labeling | Radiolabeled Nucleotides Oligonucleotides can be labeled at either the 3' or the 5' end. Using polynucleotide kinase and ATP-gamma- 32 P, the 5' end is labeled. Using terminal transferase and deoxynucleotide triphosphate labeled on the alpha phosphate, the 3' end is labeled. Traditionally, the isotope of choice has been 32 P, however 35 S has been used successfully.
Solved Classify the compound as a nucleoside or nucleotide. - Chegg Label its components and name the compound Adenine Ribo Classification: Nucleoside Deoxydenotine 5 monophosphate Nucleotide Guanine Deoxyguanosine 2.Deoxyribose monophosphate NH Deoxyguanosine Guanosine HOCHE NH Guanine Adenosine Guanonines monophosphate Nucleone ОН Ribose Adenosine monophosphate


Post a Comment for "45 nucleotide label"