43 label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution.
PDF Phase Diagrams When a second compound is introduced to the system forming a homogeneous solution however, the phase diagram drastically changes. For example, the addition of a solute to a pure solvent (making a solution) can disrupt important interactions between solvent molecules, changing the temperature at which the solvent would typically freeze or boil. 57 Features of Phase Diagrams (M11Q1) - Unizin A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. The physical state of a substance and its phase-transition temperatures are represented graphically in a phase diagram. To illustrate the utility of these plots, consider the phase diagram for water shown in Figure 2. Figure 2.
10.4 Phase Diagrams - Chemistry - opentextbc.ca A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. The physical state of a substance and its phase-transition temperatures are represented graphically in a phase diagram. To illustrate the utility of these plots, consider the phase diagram for water shown in Figure 2. Figure 2.
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution.
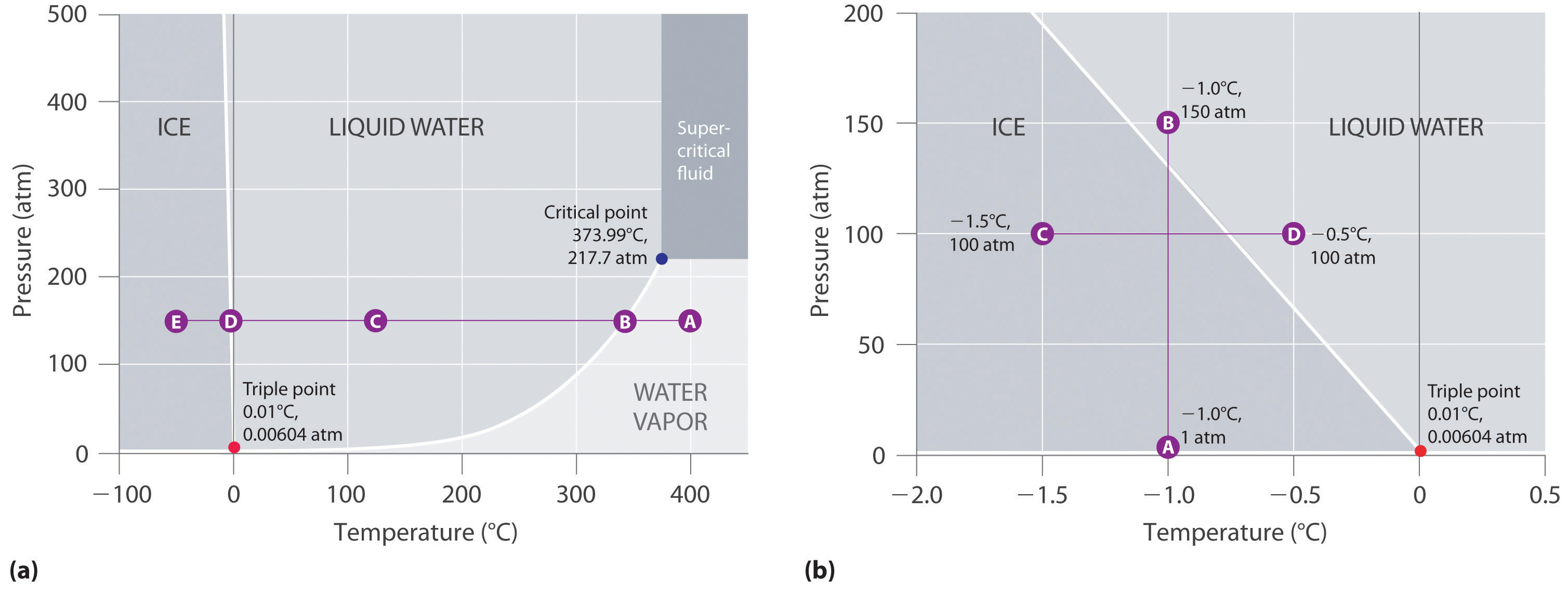
Liquid/Solid Phase Diagram - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The (solid + liquid) phase diagram for ( x1 n-C 6 H 14 + x2 c-C 6 H 12) has a eutectic at T = 170.59 K and x2 = 0.3317. A solid phase transition occurs in c-C 6 H 12 at T = 186.12 K, resulting in a second invariant point in the phase diagram at this temperature and x2 = 0.6115, where liquid and the two solid forms of c-C 6 H 12 are in equilibrium. Phase Diagrams - 2012 Book Archive The Phase Diagram of Water. Figure 11.23 "Two Versions of the Phase Diagram of Water" shows the phase diagram of water and illustrates that the triple point of water occurs at 0.01°C and 0.00604 atm (4.59 mmHg). Far more reproducible than the melting point of ice, which depends on the amount of dissolved air and the atmospheric pressure, the triple point (273.16 K) is used to define the ... Phase Diagram | Explanation, Definition, Summary & Facts Fig. 5. Another very interesting condition can be observed from the phase diagram of water i.e., if we decrease the pressure of liquid phase of water while keeping the temperature constant at a certain value, the line of lower pressure crosses the liquid phase space then solid-phase space and finally ended in vapor phase space (Fig. 6).
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution.. Answered: The phase diagrams for a pure solvent… | bartleby identify the normal freezing (fpsolv) and boiling (bpsolv) points for the pure solvent and the normal freezing (fpsoln) and boiling (bpgoln) points of the solution at 1 atm. assume the solute is nonvolatile and that the solid that freezes from solution is pure solvent. 1 atm liquid solid answer bank fpsolv bpsolv fpsoln bpsoln gas temperature … Phase Diagrams - Chemistry 2e - opentextbc.ca A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in (Figure). The physical state of a substance and its phase-transition temperatures are represented graphically in a phase diagram. To illustrate the utility of these plots, consider the phase diagram for water shown in (Figure). Phase Diagrams - Chemistry - University of Hawaiʻi A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in [link]. The physical state of a substance and its phase-transition temperatures are represented graphically in a phase diagram. To illustrate the utility of these plots, consider the phase diagram for water shown in [link]. Binary Solid-Liquid Phase Diagram | Chem Lab Introduction. Solid-liquid phase diagrams show the phase relationships in mixtures of two or more components and are very important in understanding the behavior of mixtures in metallurgy, material science and geology. In this exercise, you will measure cooling curves of either the napthalene-biphenyl system (group 1) or the napthalene-durene ...
Phase Diagram - SlideShare - The phase diagram shows two distinct phases; one is liquid metal solution and the other is solid solution. - Liquidus is that line - Above which the alloy is in liquid state - Where solidification starts - Solidus is that - Below which the alloy is in solid state, and - Where the solidification completes. PDF Binary Solid-Liquid Phase Diagram Introduction - Williams College Binary Solid-Liquid Phase Diagram Introduction The substances that we encounter in the material world are hardly ever pure chemical compounds but rather mixtures of two or more such compounds. The individual substances in such a mixture may behave more or less independent of each other but merely diluted, i.e., an ideal solution or 10.4 Phase Diagrams - General Chemistry 1 & 2 A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. The physical state of a substance and its phase-transition temperatures are represented graphically in a phase diagram. To illustrate the utility of these plots, consider the phase diagram for water shown in Figure 2. Figure 2. The phase diagram for solvent and solutions is shown in the figure ... The phase diagram for solvent and solutions is shown in the figure. What represents the normal boiling point of the solution? A A B B C C D D Hard Solution Verified by Toppr Correct option is D) The normal boiling point of the solution is that temperature at which vapour pressure of solution equals to 1 atm.
PDF phase diagram solvent solution - justonly.com phase diagram solvent solution Effect of Solute on Phase Diagram of Water SOLIDLIQUID GAS Pure solvent Freezing point of solution Freezing point of water Boiling point of water Boiling point of solution 1 atm Pressure ΔTfΔTb ΔP Temperature The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the solution ... The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the solution (non-volatile solute, dashed line) are recorded below: The quantity indicated by `L` i... Solved Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a - Chegg Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Chapter 8 Phase Diagrams - Central Michigan University Example 8.2 Interpreting a liquid-liquid phase diagram . A mixture of 50 g of hexane (0.59 mol) and 50 g nitobenzene (0.41 mol) was prepared at 290 K. ... Pure solid B begins to come out of solution and the remaining liquid becomes richer in A. (2) a 2 ® a 3. More of the solid forms, and the relative amounts of the solid and liquid (which are ...
10.4 Phase Diagrams - Chemistry A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. The physical state of a substance and its phase-transition temperatures are represented graphically in a phase diagram. To illustrate the utility of these plots, consider the phase diagram for water shown in Figure 2. Figure 2.
Solved Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a - Chegg Question: Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution Freezing point of solution GAS Solution Pure solvent 1 atm Boiling pointFreezing point of of solvent solvent ??? 11 SOLID AT AP Boiling pointLIQUID of solution Temperature This problem has been solved! See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (10 ratings)
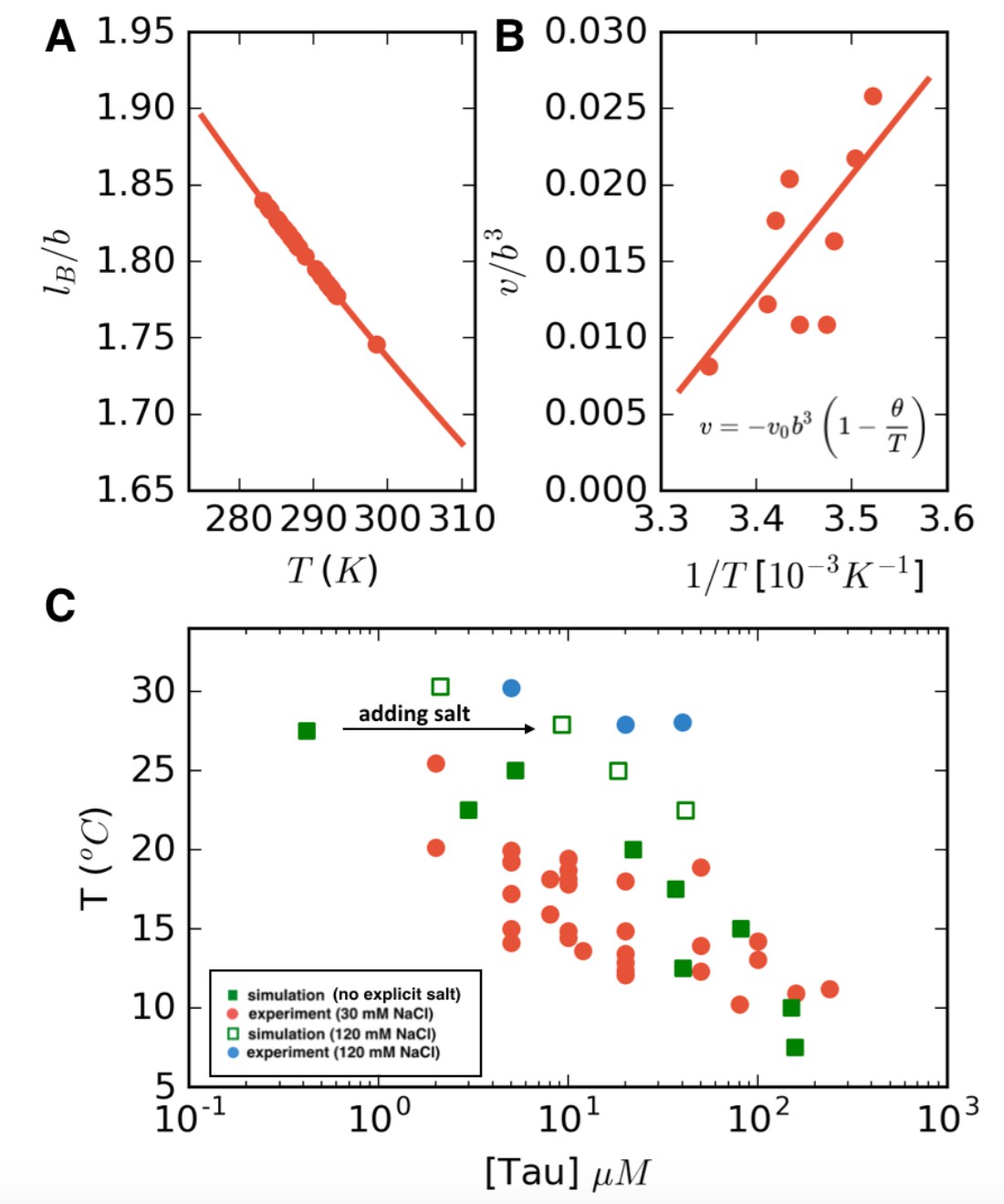
The figure shows two phase diagrams, one for a pure liquid (black line ... Similarly, the normal boiling point of the pure substance at constant pressure is indicated by C, and the raised normal boiling point of the solution with the pure liquid as the solvent (again, due to addition of nonvolatile solute to the pure liquid substance) is indicated by D, since T ↑ rightwards. ΔT b = T b − T * b = iKbm
PDF Chapter Phase Diagrams - Uttar Pradesh Textile Technology Institute A phase may be defined as a homogeneous portion of a system that has uniform phys- ical and chemical characteristics. Every pure material is considered to be a phase; so also is every solid, liquid, and gaseous solution. For example, the sugar-water syrup solution just discussed is one phase, and solid sugar is another.
solid-liquid phase diagrams: salt solution - chemguide The phase diagram for sodium chloride solution. What the phase diagram looks like. ... because adding a non-volatile solute to a solvent increases its boiling point. ... you could read the page about the phase diagrams of pure substances. Again, it isn't essential to understanding the rest of this page. You just need to be aware that the line ...
PDF Phase Diagrams, Solid Solutions, Phase Transformations Phase Diagrams: composition of phases At TA= 1320°C: Only Liquid (L) present CL= C0 ( = 35 wt% Ni) At TB= 1250°C: Both and L present At TD= 1190°C: Only Solid ( ) present C = C0( = 35 wt% Ni) C L = C liquidus ( = 32 wt% Ni) C = C solidus ( = 43 wt% Ni) 18 • Rule 3:If we know T and Co, then we know: --the amount of each phase (given in wt%).
Answered: 1) Label the LLE diagram provided… | bartleby 1) Label the LLE diagram provided indicating which component is the solvent and which is cariet, and identify the solvent rich (extract) phase boundary and the raffinate phase boundary. 2) Identify Each of the (mark as 'a', 'b', etc) following points and indicate types and number of phases present in each composition. a.
Phase Diagrams | Chemistry | | Course Hero A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in Figure 1. To illustrate the utility of these plots, consider the phase diagram for water shown in Figure 2. Figure 2. The pressure and temperature axes on this phase diagram of water are not drawn to constant scale in order to illustrate several important properties.


Post a Comment for "43 label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution."