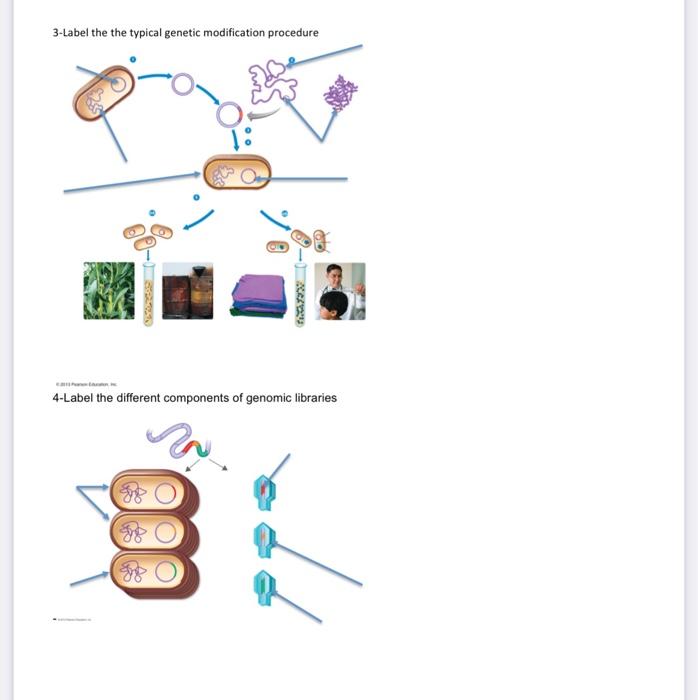
44 label the processes involved in recombinant dna technology
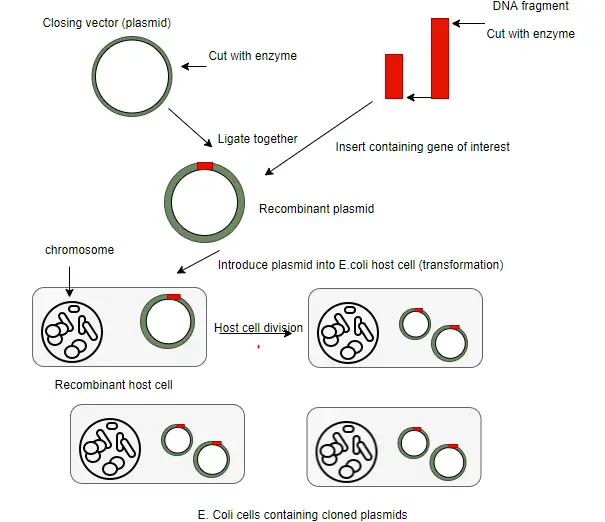
Solved Parta Label the processes involved in recombinant DNA | Chegg.com We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. SOLUTION: Proces …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Parta Label the processes involved in recombinant DNA technology Drag the appropriate Labels to their respective targets. Reset Help DNA containing eo M Culture bacteria. Recombinant DNA Technology (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion Suitable host cells are selected and the rec DNA molecule so formed [in step (iii)] is introduced into these host cells. This process of entry of rec DNA into the host cell is called transformation. Usually selected hosts are bacterial cells like E. coli, however yeast, fungi may also be utilized. (v) Selection of transformed host cells:
Chapter 8 Recombinant DNA Technology Flashcards - Quizlet Describe the process. Technique that allows DNA to be combined from different sources; also called gene or DNA splicing. Recombinant DNA is an important technique for many gene-cloning applications. 1) Isolate plasmid: probe is used to isolate the gene of interest

Label the processes involved in recombinant dna technology
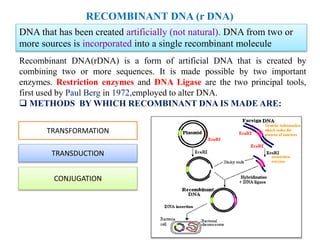
Recombinant DNA (Rdna) Technology Involves The Following Stages Recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology involves the following six stages: 1. Isolation of the Genetic Material (DNA) 2. Cutting of DNA at Specific Locations 3. Amplification of Gene of Interest Using PCR 4. Preparation and Insertion of Recombinant DNA into the Host Cell/Organism 5. Obtaining the Foreign Gene Product! 1. Processes of Recombinant DNA Technology - Toppr-guides Polymerase Chain Reaction or PCR is a method of making multiple copies of a DNA sequence using the enzyme - DNA polymerase. It helps to amplify a single copy or a few copies of DNA into thousands to millions of copies. PCR reactions are run on 'thermal cyclers' using the following components: Template - DNA to be amplified Recombinant DNA Technology Process - BYJUS Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a process to amplify the gene once the proper gene of interest has been cut using the restriction enzymes. Through this process, multiple copies of the gene of interest can be produced. PCR proceeds in three stages, denaturation, annealing and extension. Insertion of recombinant DNA into the host
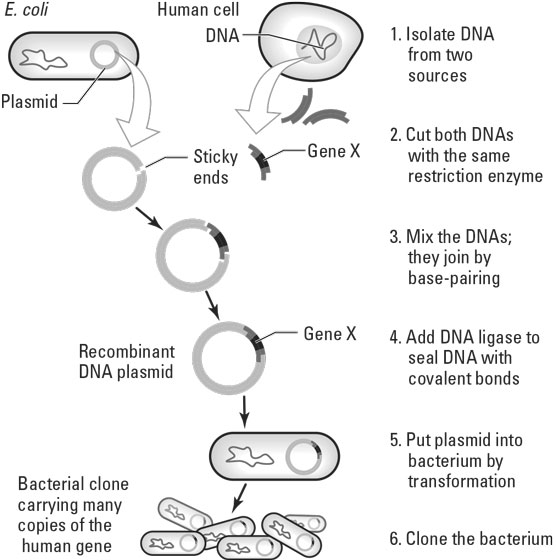
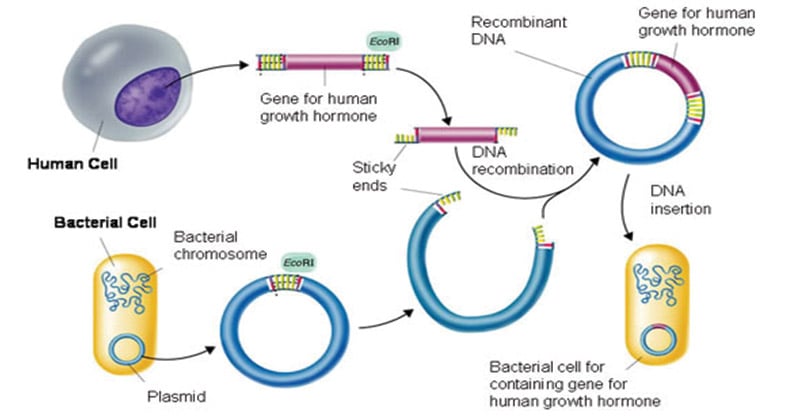
Label the processes involved in recombinant dna technology. Recombinant DNA Technology- Tools, Process, and Applications The complete process of recombinant DNA technology includes multiple steps, maintained in a specific sequence to generate the desired product. Step-1. Isolation of Genetic Material. The first and the initial step in Recombinant DNA technology is to isolate the desired DNA in its pure form i.e. free from other macromolecules. Step-2. 5 Steps in Recombinant DNA Technology or rDNA Technology We will be discussing the basic steps involved in rDNA technology, gene cloning or genetic engineering. Step1: Identification and isolation of gene of interest From where we get the desired gene? From Genomic library cDNA library Chemical synthesis of gene if we know the sequence Solved Bacterial cell ?? DNA containing gene of interest - Chegg Label the processes involved in recombinant DNA technology. Show transcribed image text Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (5 ratings) Steps of Recombinant DNA Technology Flashcards | Quizlet Isolate DNA from two sources 2. Cut both DNA with some restriction enzyme 3. Mix DNA they join by base pairing 4. Add DNA ligase to bond covalently 5. Put plasmid into bacterium by transformation 6. Identify cells containing recombinant plasmid by ability to grow in presence of ampR and tetR 7. Clone selected bacteria Methaline Blue
The different steps of recombinant DNA technology are given ... - Toppr Ask (i) isolation of the dna fragments or genes to be cloned (ii) introduction of the recombinant dna into a suitable cell (usually e.coli) called host (transformation) (iii) multiplication/expression of the introduced gene in the host (iv) selection of the transformed host cells, and identification of the clone containing the desired gene/dna … What Is Recombinant DNA Technology? - ThoughtCo Food Products . A number of food products are produced using recombinant DNA technology. One common example is the chymosin enzyme, an enzyme used in making cheese. Traditionally, it is found in rennet which is prepared from the stomachs of calves, but producing chymosin through genetic engineering is much easier and faster (and does not require the killing of young animals). Recombinant DNA Technology- Definition, Steps, Applications Polymerase Chain Reaction or PCR is a method of making multiple copies of a DNA sequence using the enzyme - DNA polymerase in vitro. It helps to amplify a single copy or a few copies of DNA into thousands to millions of copies. PCR reactions are run on 'thermal cyclers' using the following components: Template - DNA to be amplified 7 Steps Involved in the Preparation of a Recombinant DNA The following points highlight the seven steps involved in the preparation of a recombinant DNA. The steps are: 1. Selection of Target DNA 2. Selection of a Suitable Cloning Vector DNA or Vehicle DNA 3. Selection of Restriction Endonucleases 4. Procedure for Production of Recombinant DNA (rDNA) 5. Introduction of the rDNA into a Host Cell 6.
Recombinant DNA - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Recombinant DNA is the method of joining two or more DNA molecules to create a hybrid. The technology is made possible by two types of enzymes, restriction endonucleases and ligase. A restriction endonuclease recognizes a specific sequence of DNA and cuts within, or close to, that sequence. By chance, a restriction enzyme's recognition sequence ... Recombinant DNA Technology - Genome.gov Recombinant DNA technology is an extremely important research tool in biology. It allows scientists to manipulate DNA fragments in order to study them in the lab. It involves using a variety of laboratory methods to put a piece of DNA into a bacterial or yeast cell. Once in, the bacteria or yeast will copy the DNA along with its own. DNA Replication Steps and Process - ThoughtCo Step 1: Replication Fork Formation. Before DNA can be replicated, the double stranded molecule must be "unzipped" into two single strands. DNA has four bases called adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G) that form pairs between the two strands. Adenine only pairs with thymine and cytosine only binds with guanine. Principle of Recombinant DNA Technology (4 Steps) The four steps are: (1) Gene Cloning and Development of Recombinant DNA (2) Transfer of Vector into the Host (3) Selection of Transformed Cells and (4) Transcription and Translation of Inserted Gene. Knowledge about cell and its functioning has increased to a great magnitude during 20th century.
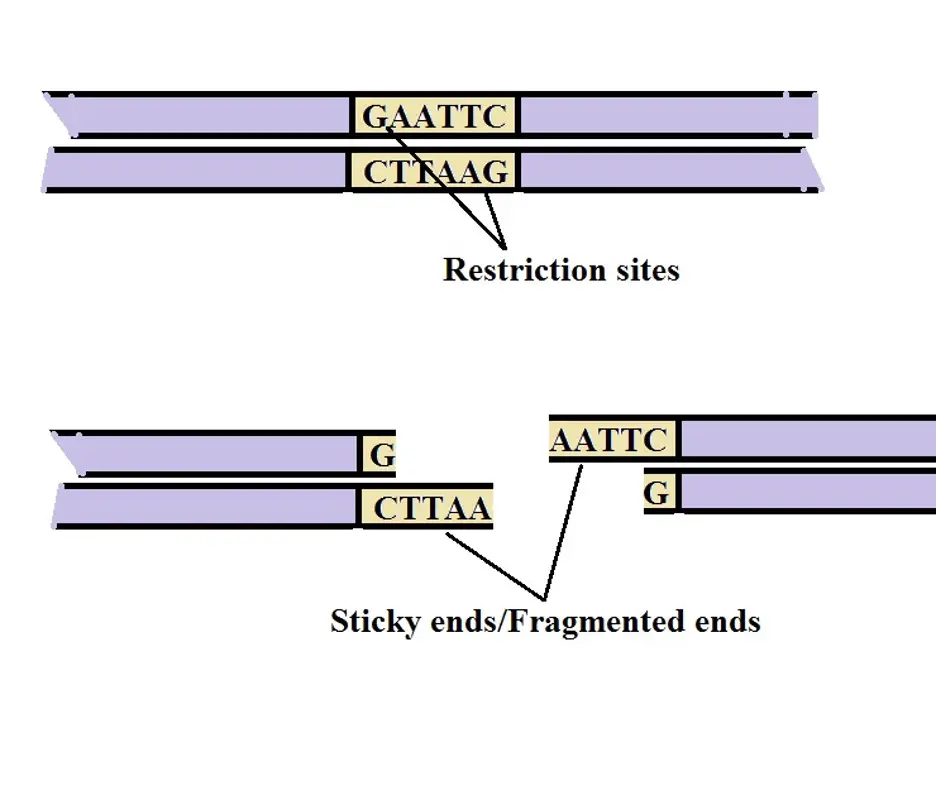
Recombinant DNA - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf The first step in the development of recombinant DNA technology was the characterization of restriction endonucleases — enzymes that cleave DNA at specific sequences. These enzymes were identified in bacteria, where they apparently provide a defense against the entry of foreign DNA (e.g., from a virus) into the cell.
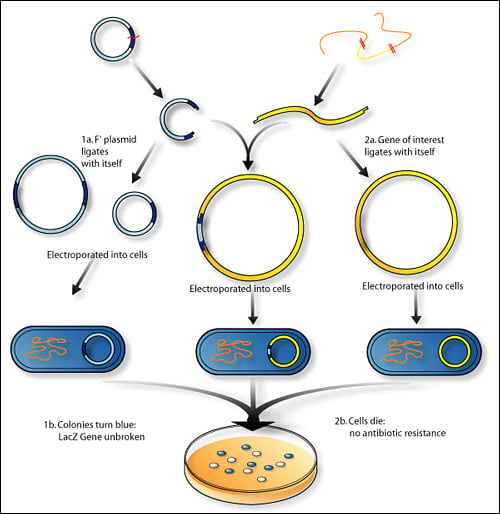
Biology - Recombinant DNA Technology Flashcards | Quizlet - INSERTION: Of the gene into a vector (carrier) e.g. plasmid - TRANSFORMATION: Transfer gene and vector into suitable host cells e.g. E coli - IDENTIFICATION: Of the host cells that have taken up the gene using gene markers - GROWTH/CLONING: Of the host cells
Micro Exam 3 Flashcards - Quizlet Label the processes involved in recombinant DNA technology. The use of microorganisms to produce useful products is known as. ... Which of the following tools of recombinant DNA technology is incorrectly paired? Gene gun: blasts DNA into target cells Vector: transposon, virus, or plasmid that carries DNA into a cell ...
Recombinant DNA technology Flashcards - Questions and Answers | Quizlet Recombinant DNA technology PLAY Match Gravity Some populations of flies are becoming resistant to insecticides intended to kill them. Scientists developed a method for finding out whether a fly was carrying a recessive allele, r, that gives resistance to an insecticide. The dominant allele, R, of this gene does not give resistance.
With the help of a neat and labelled diagram describe steps in ... The basic steps involved in the process of DNA technology are as follows. (i) The genomic DNA is isolated from a donor. (ii) Using restriction enzymes such as endonucleases the DNA is fragmented. Endonuclease enzymes are known as molecular scissors as they produce nick in the DNA fragment at the desired place. (iii) The fragments were taken out ...
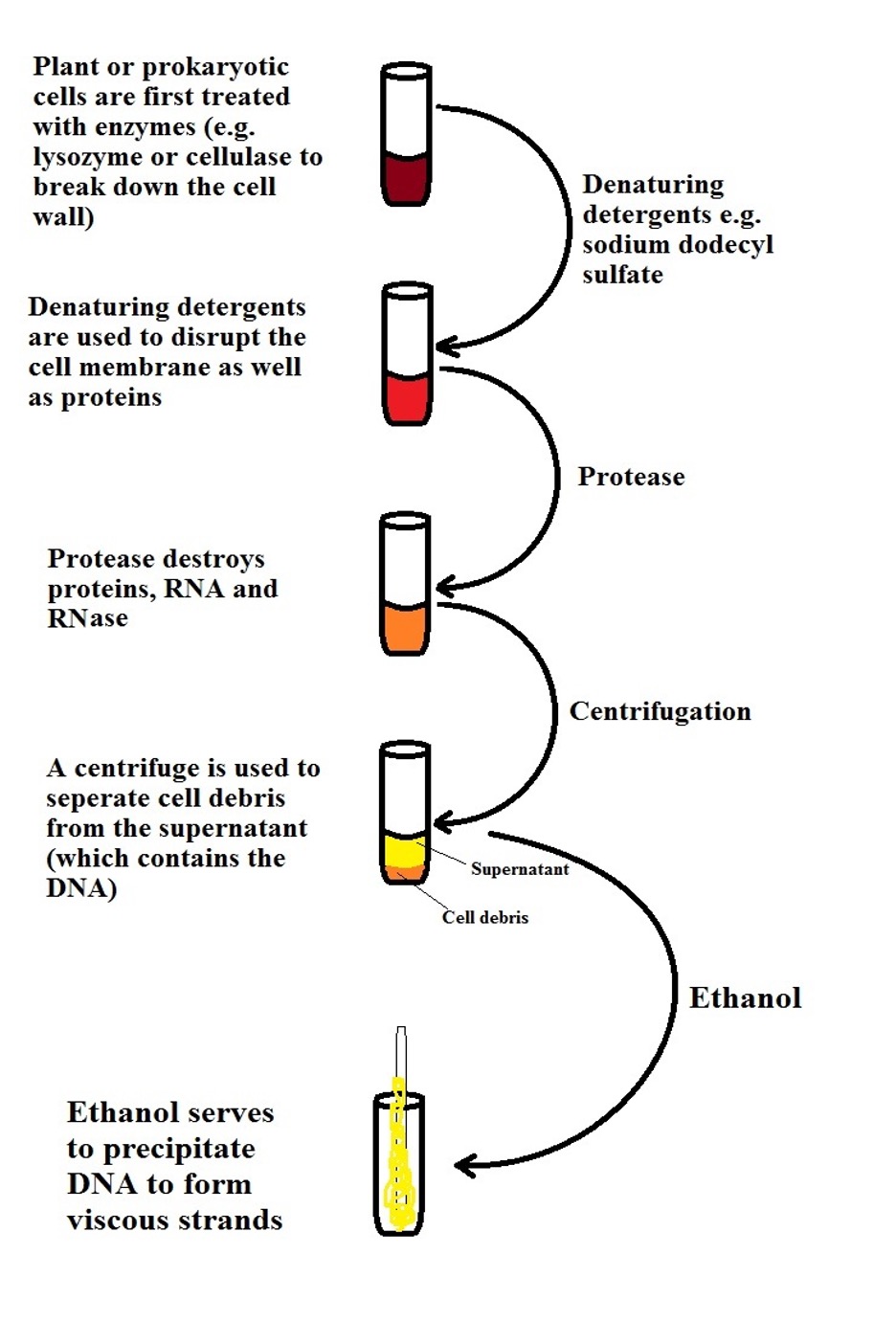
Recombinant DNA Technology - Goals, Process, Tools and ... - VEDANTU Steps of Recombinant DNA Technology 1. DNA Isolation DNA is isolated in its pure form, which means they are devoid of other macromolecules. In rDNA technology, the initial step is to extract the desired DNA in its purest form, that is, free of extraneous macromolecules.
Recombinant DNA Technology (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion The technique of recombinant DNA can be used as follows: 1. It can be used to elucidate molecular events in the biological process of cellular differentiation and ageing. 2. This can also be utilised in making gene maps with precision. 3. This can be used to spell out the complete nucleotide sequence of genome of various organisms including humans.
recombinant DNA | Definition, Steps, Examples, & Invention recombinant DNA, molecules of DNA from two different species that are inserted into a host organism to produce new genetic combinations that are of value to science, medicine, agriculture, and industry. Since the focus of all genetics is the gene, the fundamental goal of laboratory geneticists is to isolate, characterize, and manipulate genes.
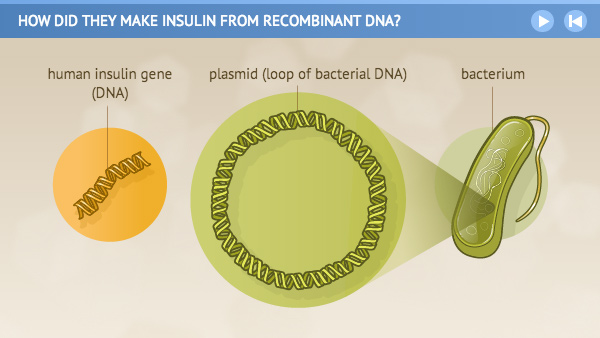
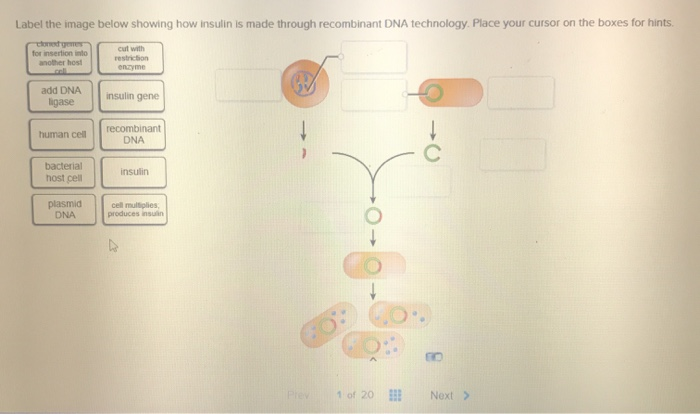
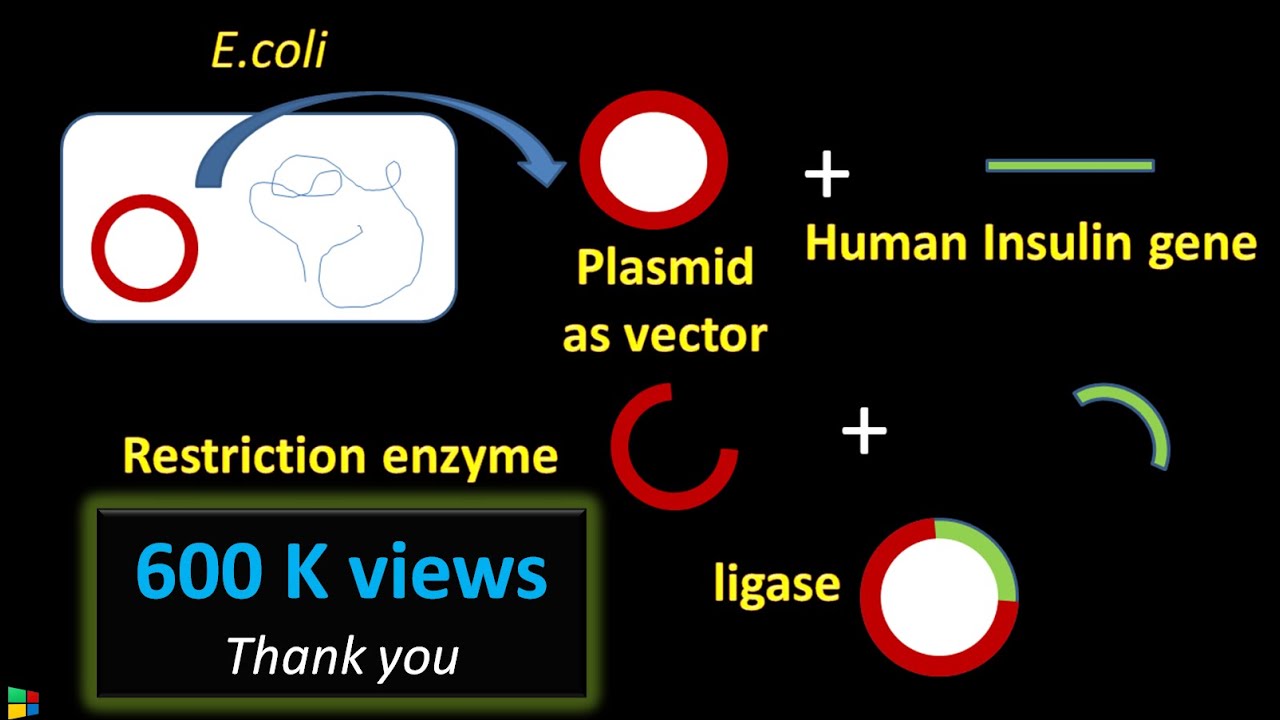
How did they make insulin from recombinant DNA? Recombinant DNA is a technology scientists developed that made it possible to insert a human gene into the genetic material of a common bacterium. This "recombinant" micro-organism could now produce the protein encoded by the human gene. Scientists build the human insulin gene in the laboratory. Then they remove a loop of bacterial DNA ...
Recombinant DNA Technology Process - BYJUS Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a process to amplify the gene once the proper gene of interest has been cut using the restriction enzymes. Through this process, multiple copies of the gene of interest can be produced. PCR proceeds in three stages, denaturation, annealing and extension. Insertion of recombinant DNA into the host
Processes of Recombinant DNA Technology - Toppr-guides Polymerase Chain Reaction or PCR is a method of making multiple copies of a DNA sequence using the enzyme - DNA polymerase. It helps to amplify a single copy or a few copies of DNA into thousands to millions of copies. PCR reactions are run on 'thermal cyclers' using the following components: Template - DNA to be amplified
Recombinant DNA (Rdna) Technology Involves The Following Stages Recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology involves the following six stages: 1. Isolation of the Genetic Material (DNA) 2. Cutting of DNA at Specific Locations 3. Amplification of Gene of Interest Using PCR 4. Preparation and Insertion of Recombinant DNA into the Host Cell/Organism 5. Obtaining the Foreign Gene Product! 1.





















Post a Comment for "44 label the processes involved in recombinant dna technology"